Learn how they differ and the benefits and use cases of each.
What’s Metro Ethernet
Metro Ethernet works primarily in layer 2 of the OSI model – the Data Link layer. It provides the transport path, or road, for data to travel along.
| # | Layer | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | Application Layer | Enables humans or software to interact with the network through applications like file sharing, email clients and databases |
| 6 | Presentation Layer | Formats, encrypts and decrypts data for the application layer |
| 5 | Session Layer | Starts, maintains and ends connections between applications |
| 4 | Transport Layer | Transfers data across the network, for example, using TCP or UDP transport protocols |
| 3 | Network Layer | Enables communication between multiple networks and determines the data’s path, for example, applying IP addresses |
| 2 | Data Link Layer | Manages connections between physically connected nodes on a network |
| 1 | hysical Layer | Transmits raw data bits over physical media like cables or wireless connections |
What’s MPLS?
Unlike Metro Ethernet, MPLS operates between layer 2 (the data link layer) and layer 3 (the network layer) of the OSI Model, also known as layer 2.5. It’s a technology that directs the data to the correct destination.
What’s the difference between Metro Ethernet and MPLS?
Metro Ethernet is a network that transports data.
MPLS is a label-switching technology that directs traffic on a network.
MPLS is typically used to create wide area networks (WANs) over long distances but may also be deployed as a routing protocol in Metro Ethernet networks. For example, many Metro Ethernet networks use MPLS to connect their backbone networks.
Here are the differences between Metro Ethernet and MPLS in more detail.
Function
MPLS is a switching technology that directs and speeds up network traffic flow. It’s often deployed in enterprise wide-area networks (WANs) or service provider environments, as well as MANs.
Routing
By contrast, MPLS operates in layer 2.5 (between the data link and network layers). It gives each data packet a label with details about its final destination. The label provides a short path to the target IP address rather than a long network address, resulting in higher traffic speeds and lower latency.
Topologies
MPLS is just a routing technology, so it can be deployed in various network topologies, including P2P, P2MP or mesh.
Scalability
Since MPLS is not dependent on a particular transport protocol, MPLS-based networks aren’t limited by distance. They can be used for regional, national or global networks with speeds from 10Mbps to 10Gbps.
Quality of Service (QoS)
However, MPLS, with its label-based technology and native support for traffic engineering, provides flexible options to meet the needs of new applications.
MPLS and VPLS
VPLS mimics the functionality of a local area network (LAN) by configuring virtual LANs. In this way, your devices are connected as if they were on the same local network, whatever the geographical distance between your sites.
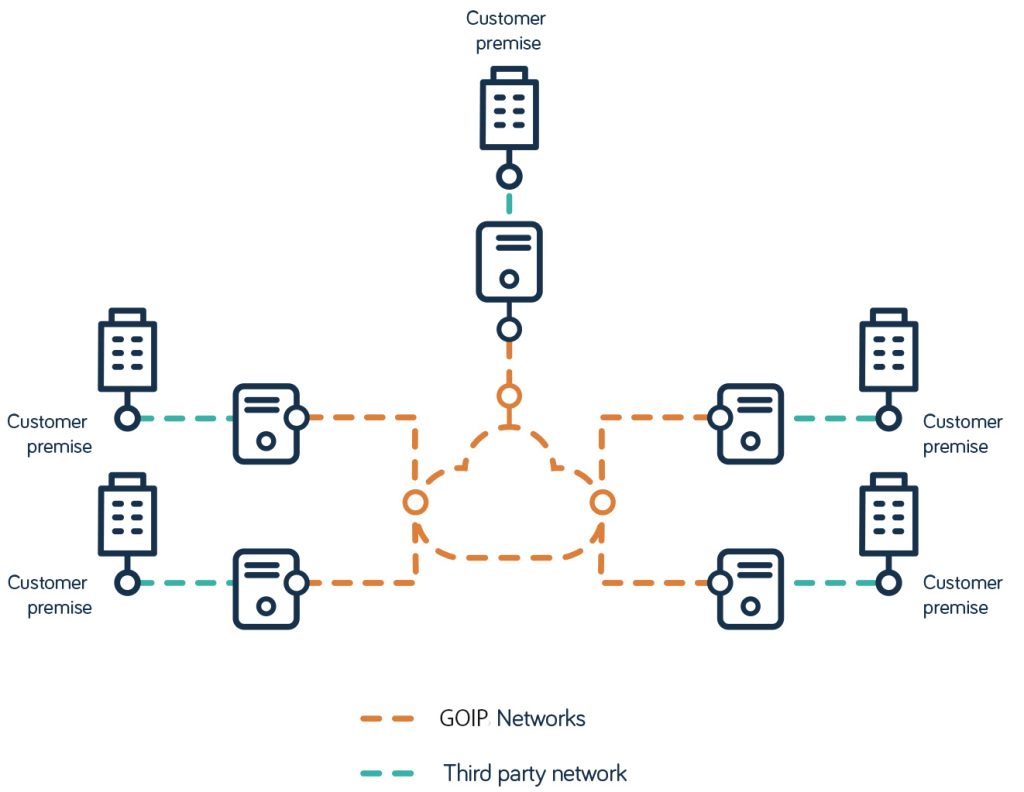
Metro Ethernet vs. MPLS: which is right for your business?
By contrast, if you want to connect more complex, geographically dispersed sites over a wide area network (WAN) with enhanced QoS and traffic engineering, an MPLS-based network may work better.
Or you could combine the two with VPLS, securely connecting multiple sites over a WAN with the reliability and performance of a local area network.
Whatever your networking needs, we can help. At GOIP, we offer a range of business Ethernet or MPLS-based network options. We’ll be happy to design a cost-effective, high-speed, secure network solution to interlink your sites.







